|
Lenses
|
Materials
|
Illustration
|
Property and Application
|
|
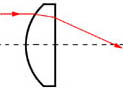
Plano-Convex
|
BK7
Fused Silica
Sapphire
CaF2
|
|
Positive focus length. Most suitable where one conjugate is more than five times the other, e.g. in sensor application or for use with near collimated light. Also where both conjugates are on the same side of the lens, e.g. as an add-on lens to increase the numerical aperture.
|
|
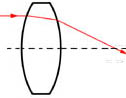
Double-Convex
|
BK7
Fused Silica
|
|
Most suitable where the conjugates are on opposite sides of the lenses and the ratio of the distances is less than 5:1, e.g. as simple image relay components.
|
|
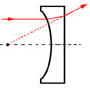
Plano-Concave
|
BK7
Fused Silica
Sapphire
CaF2
|
|
Negative lens with the form most suitable where one conjugates is more than five times the other, e.g. producing divergent light from a collimated input beam.
|
|
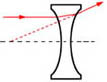
Double-Concave
|
BK7
Fused Silica
|
|
Negative lens with the form most suited to producing diverging light or a virtual image, where the input light is converging.
|
|
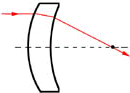
Meniscus
|
BK7 Positive
|
|
These lenses may be used to increase the numerical aperture of a positive lens assembly, without an undue increase in the aberrations.
|
|
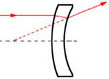
BK7 Negative
|
|
The best lens form where one conjugates is relatively far from the lens or where both conjugates are the same size of the lens.
|
|
Cylindrical
|
BK7
Fused Silica
|
|
Used to provide focusing power in one section only. For illumination or detection of light from line sources. Also used to anamorphic compression of beams and images.
|
|
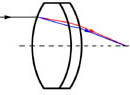
Achromatic
|
Combinations of Two Optical Grade Glasses
|
|
These lenses have considerably reduced values of spherical aberration. Coma and chromatic aberration. Best used to replace single components where performance must be improved.
|
|
Ring Mount for Lenses
|
Black Anodized Aluminum
|
|
Used to fix position of lenses.
|